Think of a constant as a place to store a value in the NXTs built-in memory. Other programming blocks can read the constant’s value by connecting to the block with data wires.
This block works like a Variable Block, but on a global basis. If you define a constant in your Define Constants from the Edit menu, you can use it with all of your programs. A constant never changes over time, like Pi (3.14), which is the mathematical constant for the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter.
Table of Contents:
Display Settings

- Name of the Constant block.
- The block’s data hub will open automatically when the block is placed in the work area. At least one data wire must be dragged from the block’s output plug to another block’s data hub. (See the Data Hub section below for more information.)
Edit Constants
To create a new constant or edit an existing one, you must first choose the Define Constant in the Edit menu of the software.

- To create a new constant, choose Create.
- To edit or delete an existing constant, highlight it on the list and choose Edit or Delete.
- Give your new constant a short, easy-to-understand name.
- Set the type of data that the constant will hold (Text, Number, or Logic).
- Depending on the data type selected, define the value of the constant as a logic, number or text value.
Configure the Constant Block

- Choose the mode for the Constant block: Choose from List or Custom
- Choose a constant from the list of existing constants. To create a new constant for this list, choose Define Constant in the Edit menu.
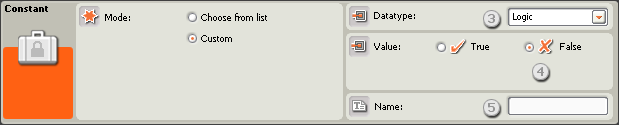
- Set the type of data that the custom constant will hold (Text, Number, or Logic).
- Choose if the define the Text, Number or Logic Value depending on the data type.
- Use the input box to enter a name for the custom constant
Sharing Information between a Program and My Block
In order to share data between your main program and a My Block (i.e., between two .rbt files), do these two things:
- Define a constant with the same name and data type in both the main program and in My Block.
- Use that constant in a Constant Block in the main program and in My Block.
Configuring the Constant Block’s Data Hub
You can control the Constant Block dynamically by connecting data wires (from other block’s data hubs) to the Constant block's data hub.
Open a block's data hub by clicking the tab at the lower left edge of the block after it has been placed on the work area.

Data wires carrying input information to a block are connected to the plugs on the left side of its data hub. Data wires carting output information are connected to the plugs on the right side.
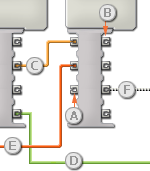
Passing data from the input plug to the output plug
If an input plug has a corresponding output plug (see A above), the input data will pass through from the input plug to the output plug without being changed. In this case, you can only use the output plug if the input plug is connected to an input data wire; connecting an output data wire to such an output plug without a connected input data wire will cause the output data wire to be "broken" (and colored gray).
Data wires carry specific types of data
Each data wire carries a specific type of data between blocks. For example, if a data wire is dragged from a logic plug on a block’s data hub, it can only be connected to a logic plug on another block’s data hub. The chart below shows what kind of data each plug can accept or send out.
Data wire colors
Data wires are identified with specific colors: wires carrying number data are colored yellow, wires carrying logic data are colored green, and wires carrying text data are colored orange.
"Broken" data wires
If you try to connect a data wire to a plug of the wrong data type, the data wire will be broken (and colored gray). You will not be able to download your program if a data wire is broken.
If you click a broken wire you can read why it is broken in the small help window in the lower right corner of the work area.
Data must be within the possible range of the plug
If an input data wire transmits a value outside the possible range of the plug it is connected to, the block will either ignore the value or change it to a value within its range. For plugs that allow just a few input values (example: just 0, 1, or 2), the plug will ignore the input if a value arrives outside its range.
For plugs that accept larger input ranges (example: 0 – 100), the plug will force any input outside its range to fit. For example, if a Move block’s Power plug receives an input value of 150, the block will change the input value to 100 (i.e., a number within the Power plug’s range).
This chart shows the different characteristics of the plugs on the Constant Block’s Data Hub:
| Plug | Data Type | Possible Range | What the Values Mean | This Plug is Ignored When... | |
| Logic | True / False | ||||
| Number | Number | ||||
| Text | Text |